
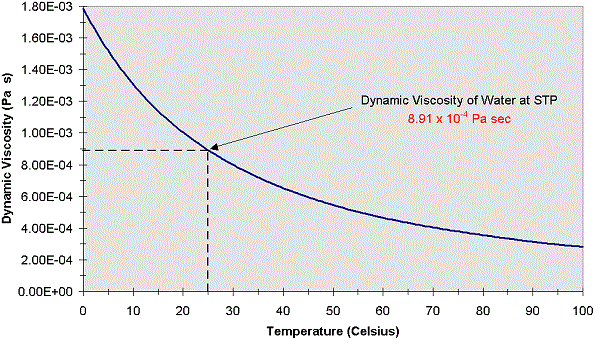
Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of the viscosity of a fluid to its density. Dynamic viscosity is just as the same as normal viscosity of sesistance of fluid. There are two types of viscosity one is Dynamic viscosity and kinematic viscosity. Its form can be motivated by modeling momentum transport at the molecular level as an activated rate process, although the physical assumptions underlying such models have been called into question. Viscosity is also based heat and shear of the fluid like water, milk and some edible oil. At its melting point, the viscosity of glass is about 10 Pa s, while this increases by a factor of 100 at its working point and by a factor of more than 10 11 at its. Molten glass is one of the most viscous fluids there is with a high viscosity approaching infinity as it solidifies. It accurately describes many liquids over a range of temperatures. XXXII Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of Air and of Exhaust Gases Between 50 and 900 F. The air you breathe has a viscosity of about 18 Pa s. This equation was first proposed in 1913, and is commonly known as the Andrade equation (named after British physicist Edward Andrade). At 25 C, the viscosity is 18.6 Pas and the kinematic viscosity 15.7 cSt. The kinematic viscosity of air at 15 C is 1.48 × 10 -5 m 2 /s or 14.8 cSt. The Lennard–Jones model predicts a more complicated T The viscosity of air depends mostly on the temperature. Air viscosity in between -100 and 500°c How the air viscosity change with temperature The air viscosity depends on the temperature and is increasing with the temperature. The predictions of the first three models (hard-sphere, power-law, and Sutherland) can be simply expressed in terms of elementary functions. The viscosity of air, at atmospheric pressure is the following : Air viscosity at 0°c 0.01722 mPa.s Air viscosity at 25°c 0.0186 mPa.s 2. The viscosity predictions for four molecular models are discussed below. In particular, given a model for intermolecular interactions, one can calculate with high precision the viscosity of monatomic and other simple gases (for more complex gases, such as those composed of polar molecules, additional assumptions must be introduced which reduce the accuracy of the theory). Those like ether or gasoline which flow very readily have low viscosities. Liquids which flow very slowly, like glycerin or honey, have high viscosities. The resistance to such flow is called the viscosity. The theoretical basis of the kinetic theory is given by the Boltzmann equation and Chapman–Enskog theory, which allow accurate statistical modeling of molecular trajectories. Viscosity Vpn Viscosity For Air 210c Because its molecules can slide around each other, a liquid has the ability to flow. The kinetic theory of gases allows accurate calculation of the temperature-variation of gaseous viscosity.
See also: Kinetic theory of gases and Chapman–Enskog theory viscosities of eight common gases including nitrogen and air over the temperature range of 90 to. However, depending on the corresponding change in density, the dynami.
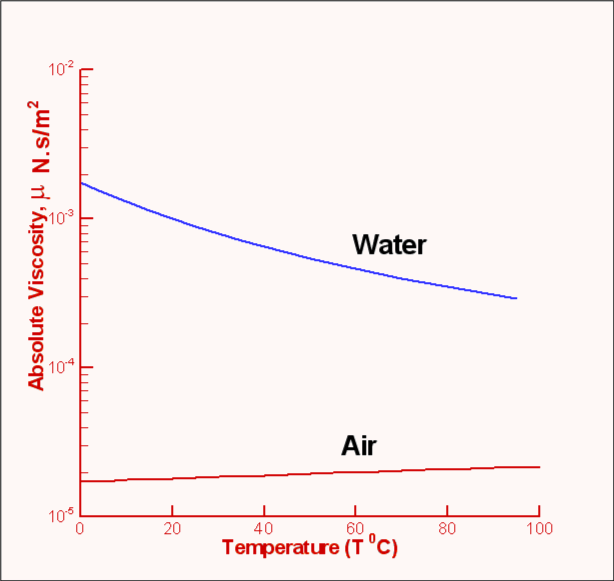
An everyday example of this viscosity decrease is cooking oil moving more fluidly in a hot frying pan than in a cold one. relating the reference dry air viscosity values to the. Answer (1 of 3): The kinematic viscosity (aka momentum diffusivity) will likely fall if air bubbles are present because the bubbles will interfere with the diffusion of momentum by collision between the molecules of the liquid. Increasing temperature results in a decrease in viscosity because a larger temperature means particles have greater thermal energy and are more easily able to overcome the attractive forces binding them together. In liquids, viscous forces are caused by molecules exerting attractive forces on each other across layers of flow. Hence, gaseous viscosity increases with temperature.
#Air viscosity free
Since the momentum transfer is caused by free motion of gas molecules between collisions, increasing thermal agitation of the molecules results in a larger viscosity. This transfer of momentum can be thought of as a frictional force between layers of flow. Viscosity in gases arises from molecules traversing layers of flow and transferring momentum between layers.
Viscous drag causes the rapid deceleration of fungal spores after high-speed launches and limits discharge distance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
